Lobbying at the federal level — at a glance
PDF version (1.48 MB, 2 pages)
Regulated lobbying is:
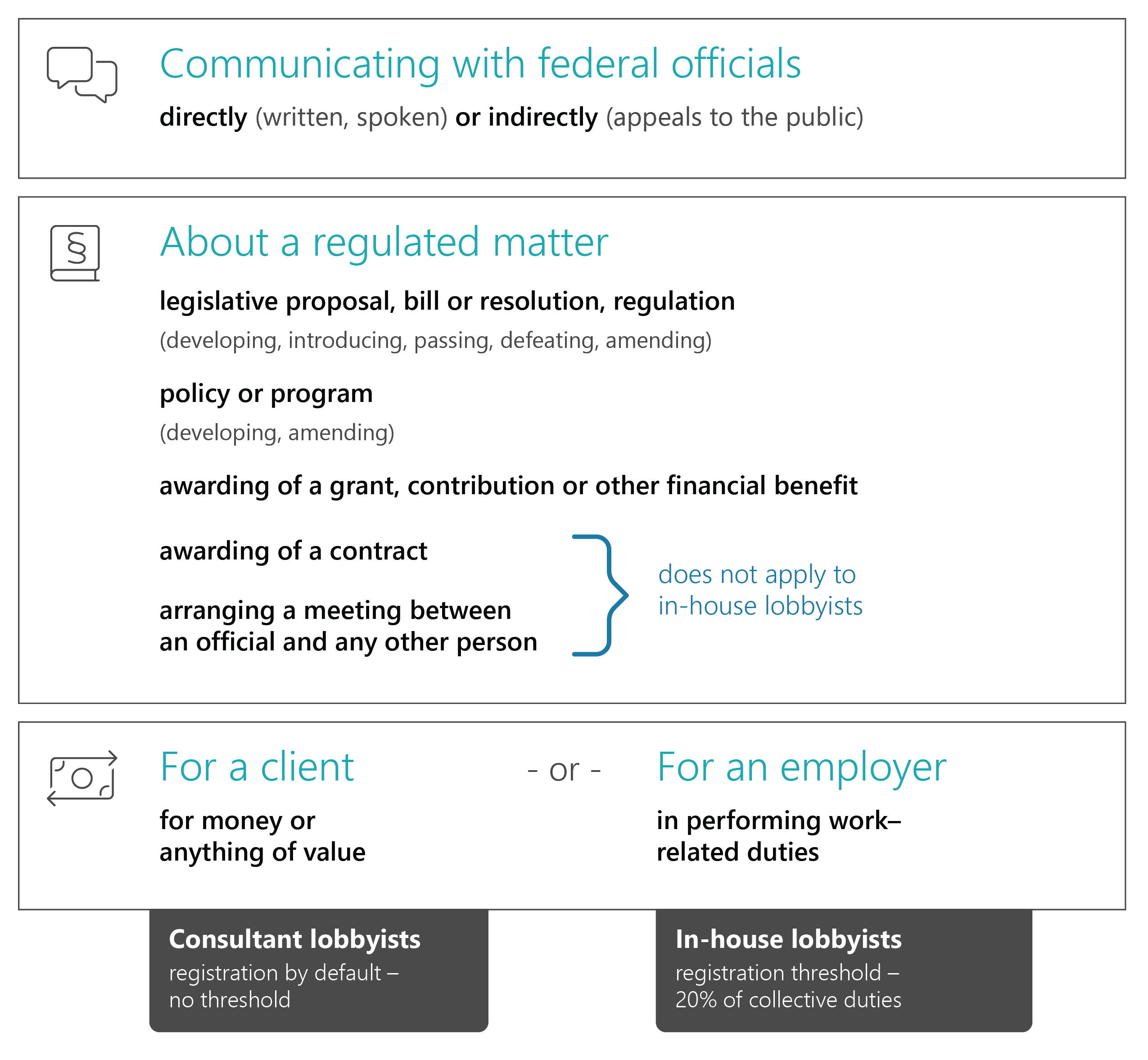
Text version
Communicating with federal officials directly (written, spoken) or indirectly (appeals to the public)
About a regulated matter
legislative proposal, bill or resolution, regulation
(developing, introducing, passing, defeating, amending)
policy or program
(developing, amending)
awarding of a grant contribution or other financial benefit
awarding of a contract*does not apply to in-house lobbyists
arranging a meeting between an official and any other person*does not apply to in-house lobbyists
For a client for money or anything of value (Consultant lobbyists registration by default – no threshold)
or
For an employer in performing work-related duties (In-house lobbyists registration threshold – 20% collective duties)
Communications that are not regulated
- a request limited to asking for information
- asking an official how a law or regulation is enforced, interpreted or applied
- making a public submission to a parliamentary committee or in public record proceedings, such as before a board, commission or tribunal
Those who lobby
Consultant lobbyists
- individuals, including external board members, who lobby on behalf of a client
- must register individually for each client in the Registry of Lobbyists
In-house lobbyists
- employees who lobby on behalf of their employer
- must be registered by the employer in a single registration once collective lobbying reaches the in-house lobbyist registration threshold:





Collectively 
Excludes:
- employees of a corporation or organization not meeting the registration threshold
- citizens communicating solely on their own behalf
- officials from other levels of government
- volunteers doing advocacy that is not for the benefit of their employer or client
Those who are lobbied
Lobbying any federal official (public office holder) is subject to the Lobbying Act and may require registration and the filing of returns in the Registry.

Text version
Officials
- almost all federal employees, officers and executives
- members of the Armed Forces and RCMP
- staff of parliamentarians
- plus all designated officials
Designated officials
- all parliamentarians – Senate and House of Commons – including the Prime Minister, ministers and ministers of state
- ministerial staff
- most senior executives - deputy ministers, CEOs, associate and assistant deputies, etc.
- additional positions set by regulation
Additionally, most arranged and spoken lobbying communications with a designated official (designated public office holder) must be filed in the Registry.
Five-year lobbying restriction
A designated official is restricted from lobbying for 5 years once they stop performing the duties of their designated position.
During the restriction period, a former designated official cannot:
- lobby for a client for money or anything of value
- lobby on behalf of an organization that employs them
- lobby on behalf of a corporation that employs them, if lobbying constitutes a significant part of their work (20% or more)
Lobbyists' Code of Conduct
The Code sets standards of behaviour for lobbyists and works alongside the ethical regimes that apply to federal officials.
All regulated lobbyists must apply the Code's rules in their lobbying and interactions with officials they lobby or expect to lobby.
By complying with the Code’s rules, lobbyists:
- strengthen the ethical culture of lobbying
- avoid placing officials in real or apparent conflict of interest situations
- contribute to public confidence in the integrity of federal government institutions and decision making
Registry of Lobbyists
The Registry is a searchable database of all registered lobbying that enables transparency. It provides statistics and access to several reports.
Registrants must respect the disclosure requirements and timelines set by the Lobbying Act and its regulations – failure to file information or file on time is an offence.
Non-compliance
Concerns of federal lobbying requirements not being respected can result in compliance measures, including monitoring and investigation.
Failing to comply with the Lobbying Act is an offence. Anyone convicted of an offence may be subject to penalties – including fines, imprisonment, and/or a lobbying ban.
Any finding of non-compliance with the Lobbyists’ Code of Conduct is reported to Parliament.
- Date modified:
